Model Specifications
Production Process:
Model Components:
Outfit Model Components: Clothing models are divided into five separate parts: top, bottom, shoes, gloves, and hair. Each part is independently crafted.
Hair: If segmentation of front and back hair is not required, it can be produced as a complete hairstyle.
Interchangeability: All outfit components must adhere to customization standards to ensure that different pieces can be mixed and matched seamlessly.
Skin Part of the Model: Modifications to the UV and the seams where the clothing meets the skin are not permitted; however, other areas can be adjusted freely.
Material IDs: Skin and clothing sections must have distinct material IDs.
Material Slots: Each clothing part, including skin materials, can support up to three material slots.
Recommended Polygon Counts:
- Inclusive of Integrated Base Model: The recommended polygon counts should include the base model parts merged with the clothing components.
- Hair Models: You can choose one of three methods for crafting hair models: front hair + back hair, complete hairstyle, or strand-based hair.
| Top + Body Base Model | Gloves + Hand Base Model | Bottom + Leg Base Model | Shoes + Foot Base Model | Regular Hairstyle + Accessories | Strand-based Hair + Accessories | Complete Set | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| External Model | Max Polygons | 10,000 | 3,500 | 4,000 | 3,500 | 7,500 | 10,000 | 30,000 (approx.) |
| Internal Model | Max Polygons | 2,500 | 1,500 | 1,700 | 1,500 | 2,500 | 3,000 | 10,000 (approx.) |
Model Production Guidelines:
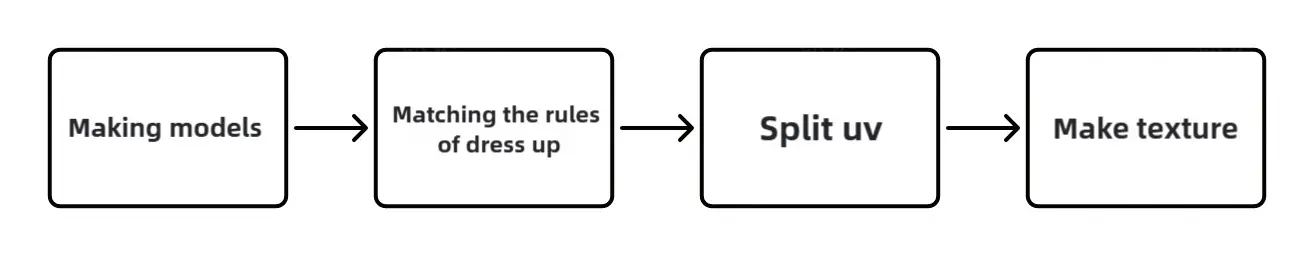
Base Model Alignment: Ensure that clothing components align precisely with the base model's wireframe to prevent clipping. This alignment is crucial for the visual integrity and functionality of interchangeable outfit parts.
Costume Split Lines: Align clothing parts with the base model's designated costume split lines to ensure seamless compatibility with outfit swapping rules. Avoid any clipping near these lines, ensuring that clothing meshes integrate flawlessly with the base model's topology.
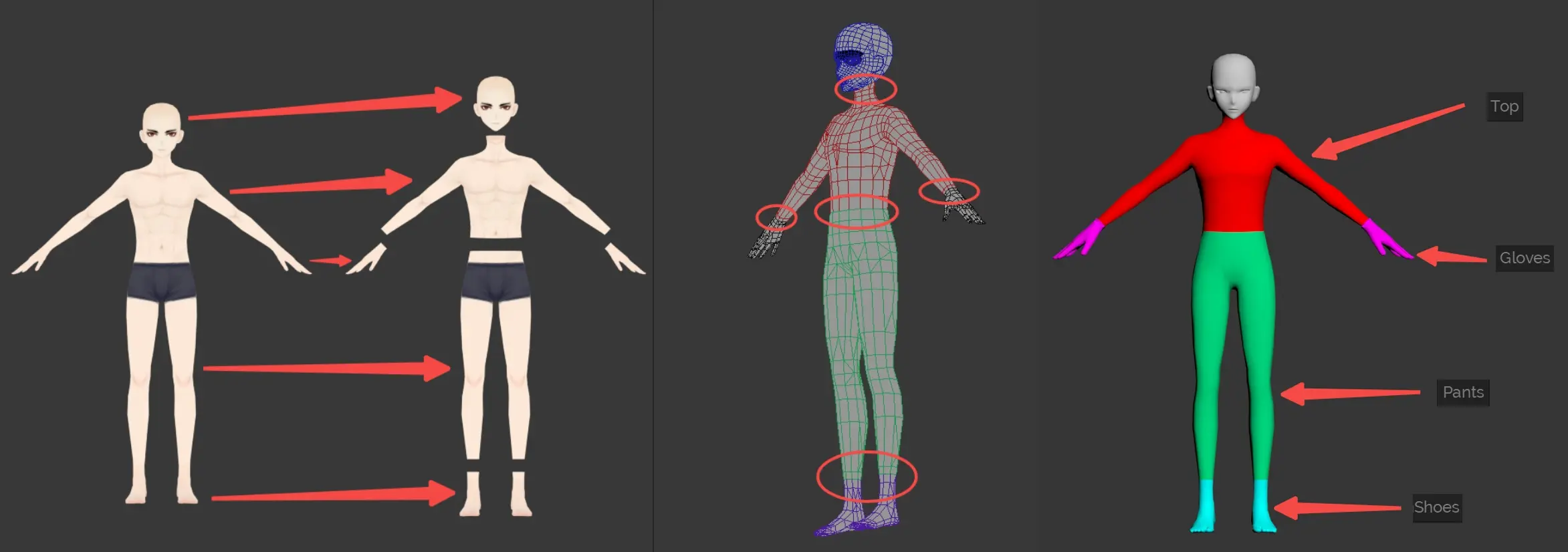

Model Usage: Utilize models within the outfit rules strictly for dimensional reference. They should not serve as guidelines for wireframing or design styling.
Mesh Removal: Remove any part of the base model mesh that is obscured by clothing. Ensure that the joining points between clothing and the base model are precisely aligned and welded to create an imperceptible junction.
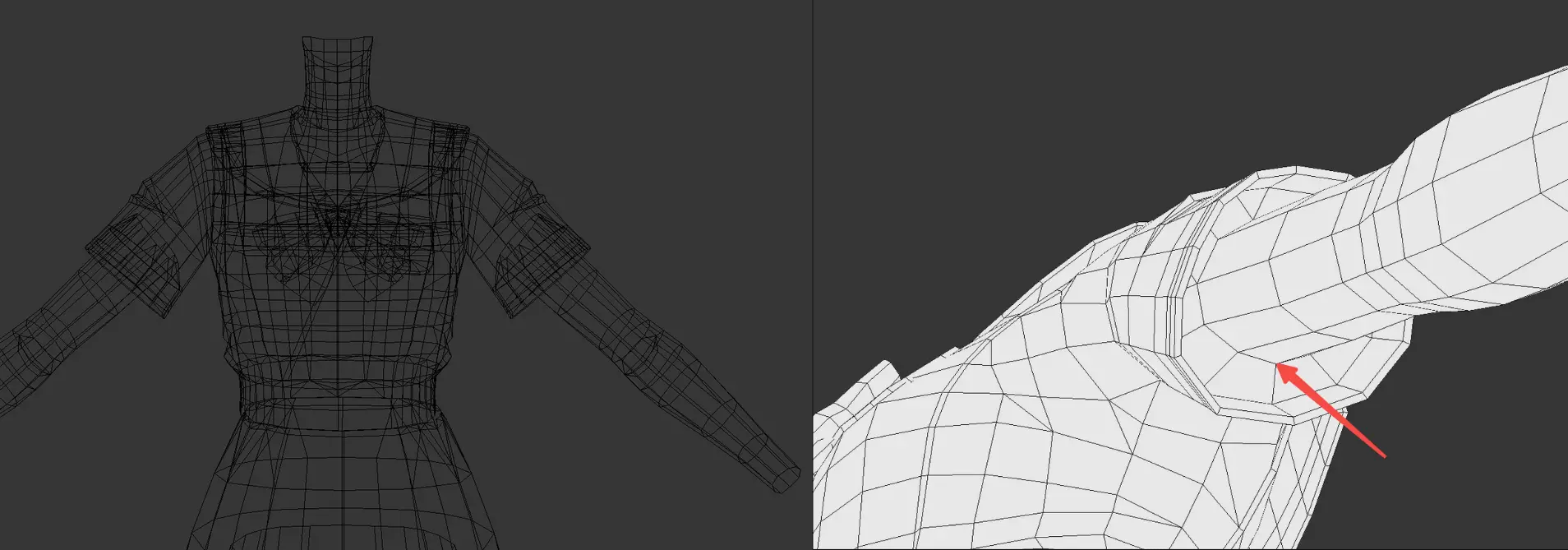
Double-Sided Display: By default, materials do not support double-sided display. To achieve this effect, replicate the model and invert it to simulate double-sidedness.
Vertex Color Alpha Check: Post-model completion, ensure the vertex color alpha is pure white. Deviations can lead to visual discrepancies, such as misplaced edge highlights during gameplay.
Modeling Tips
Smooth Group Settings
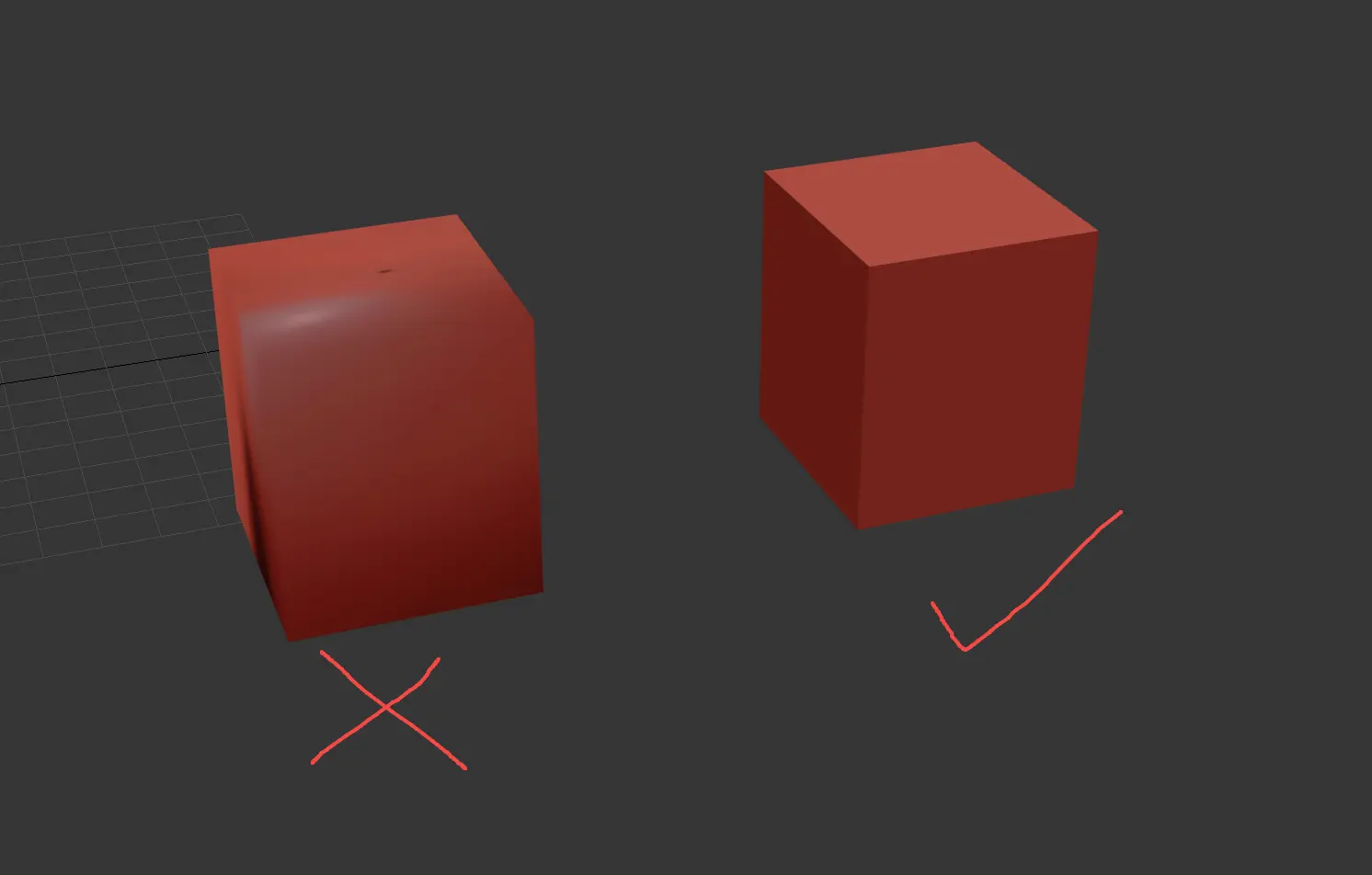
- Optimize Visual Appeal: Setting smooth groups correctly can significantly enhance the model's appearance, promoting a more realistic interplay of light and shadow.
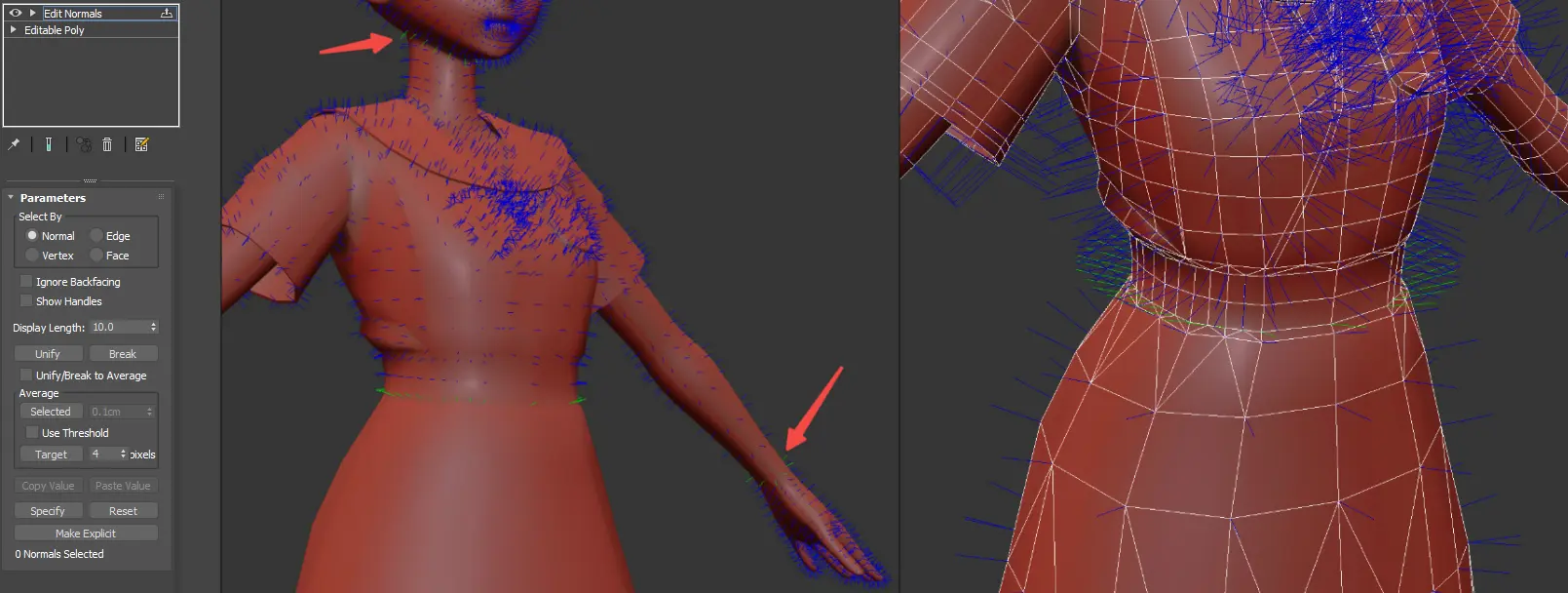
Eliminating Body Seams
- Normal Consistency: Discrepancies in normals between the clothing and the base model can lead to visible seams at the joints.
- Normal Editing: Employ the 'Edit Normals' function in 3ds Max to standardize normals across the model, ensuring that normals at the seams of interchangeable parts are perfectly matched.
Clothing Component Customization Standards
Top Section
Top Range: (Refer to the outfit range document for reference.)
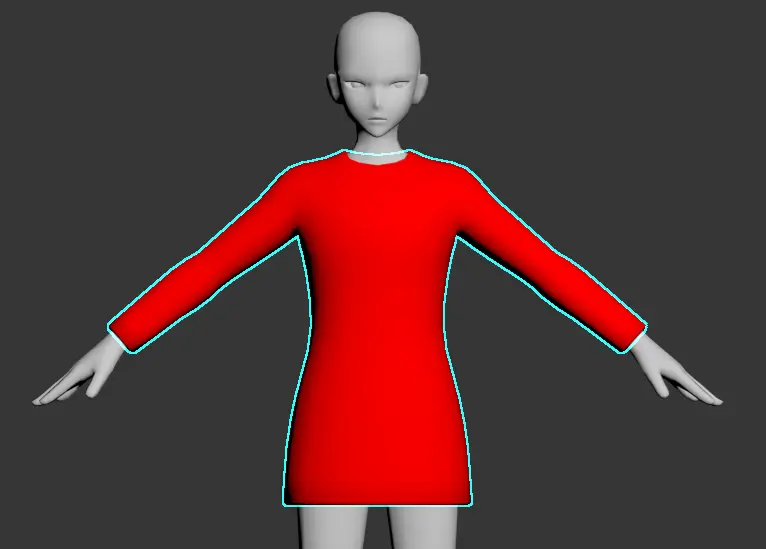

Top and Bottom Models: If the top and bottom models do not extend to the base model's split line, the base model should be used to complete the missing sections.
Junctions Between Base Model and Clothing: Vertices at the junctions of the base model and clothing must be welded together.

Belts and Pants: Must be designed to match the range of the top section.

- Top Components: Must be completely covered by the top section's designated range.
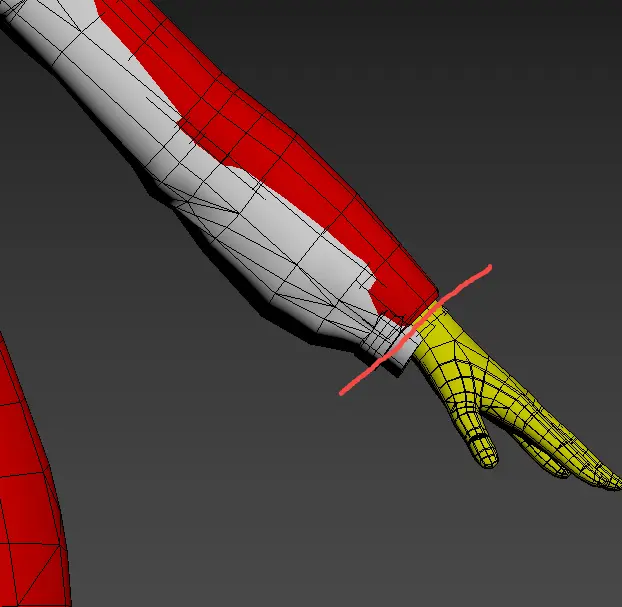
- Wrist Joint Line: Must align with the boundary of the top section.
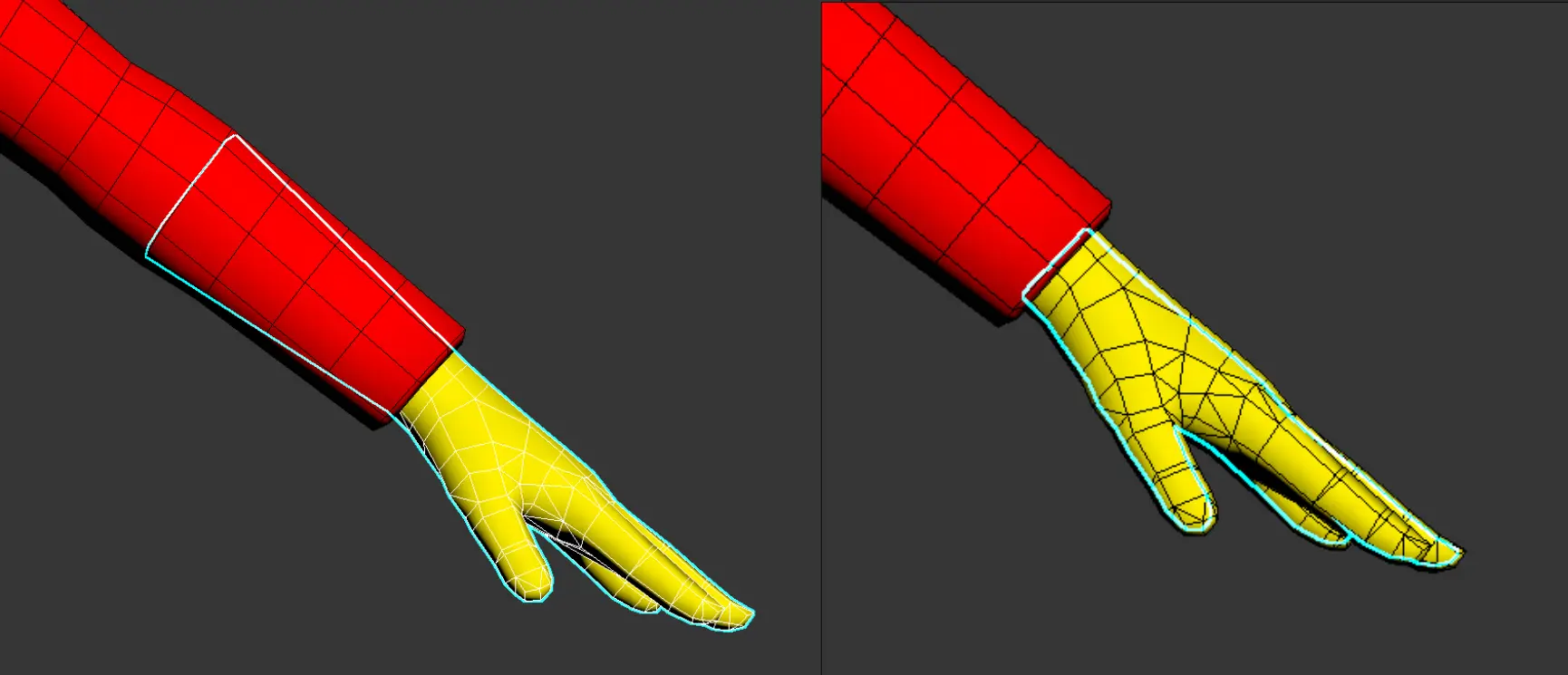
- Sleeves: Must encompass the range of the gloves.
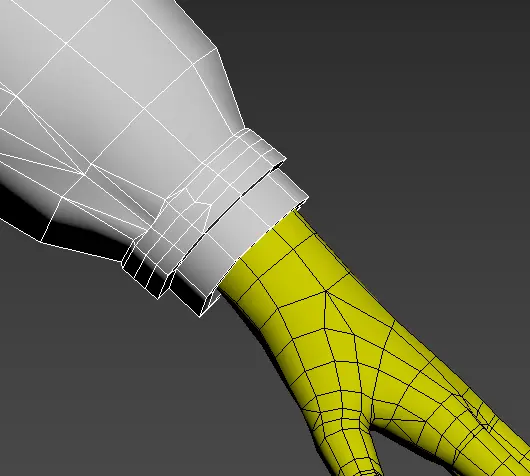

Bottom Section
- Socks and Shoes: When socks or shoes extend above the knee, the part of the sock above the base model's leg split line is categorized as a bottom component.
- Once categorized as a bottom component, the bottom seam must align perfectly with the base model's cut (must be exactly the same).
- The area around the knee and below must maintain alignment with the base model's topology.

- Clothing Wireframe: Regular clothing wireframe should align with the direction of the base model's wireframe to avoid visual inconsistencies.
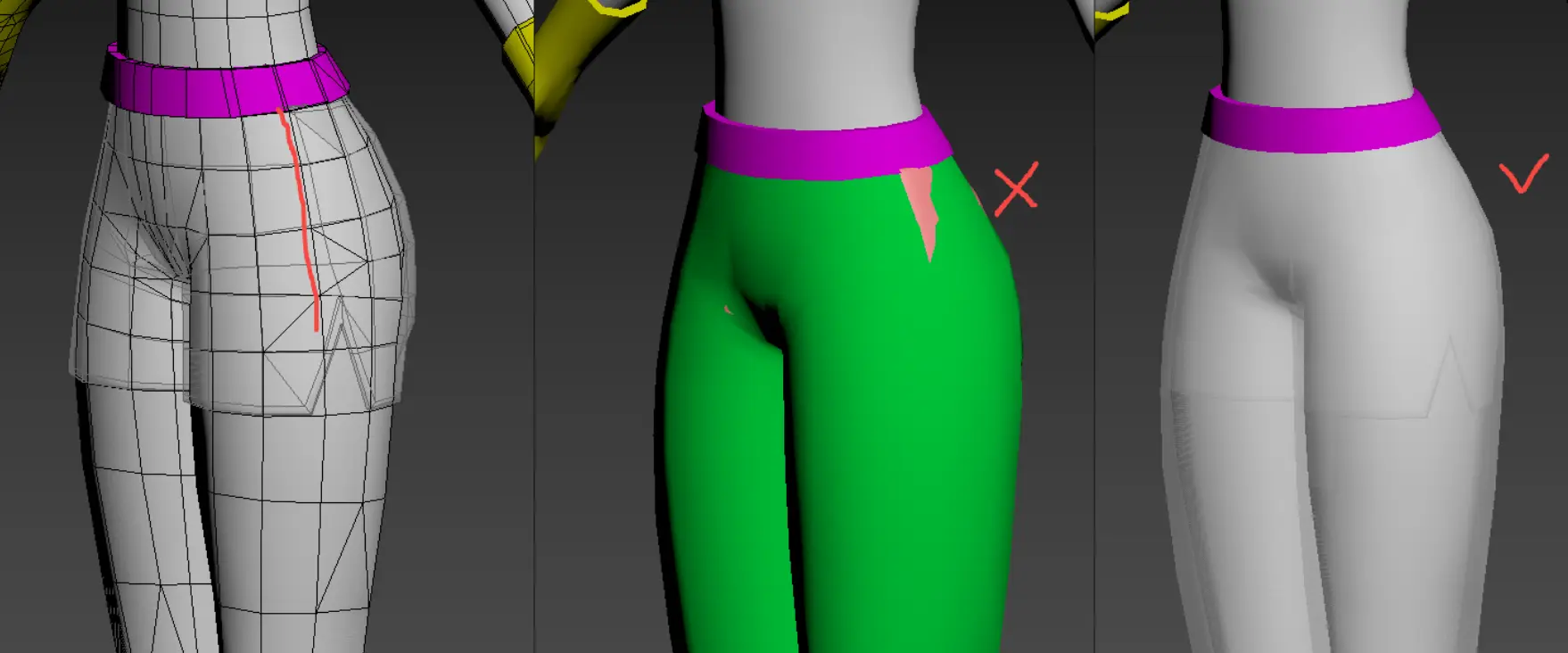

- Belt and Pants Coverage: Bottom garments should be covered by both the belt's and pants' designated ranges.
- The belt must be encompassed within its specified range.
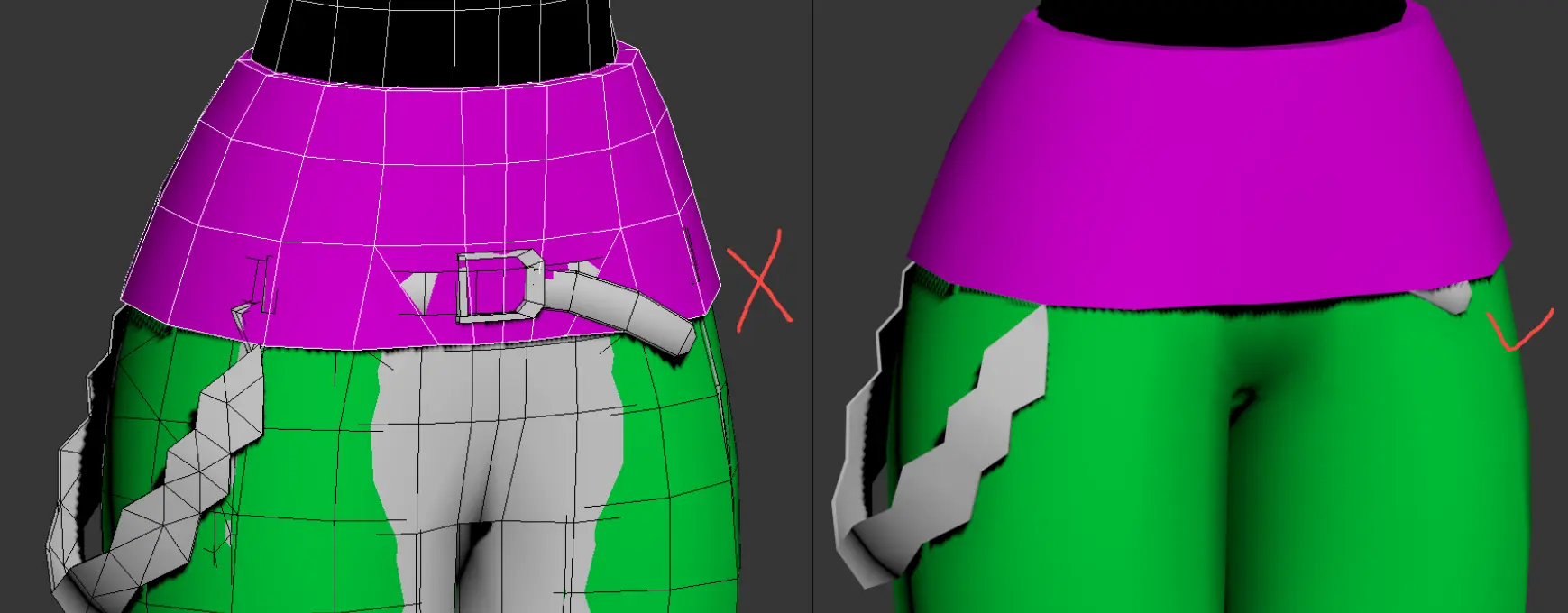
Shoes Section
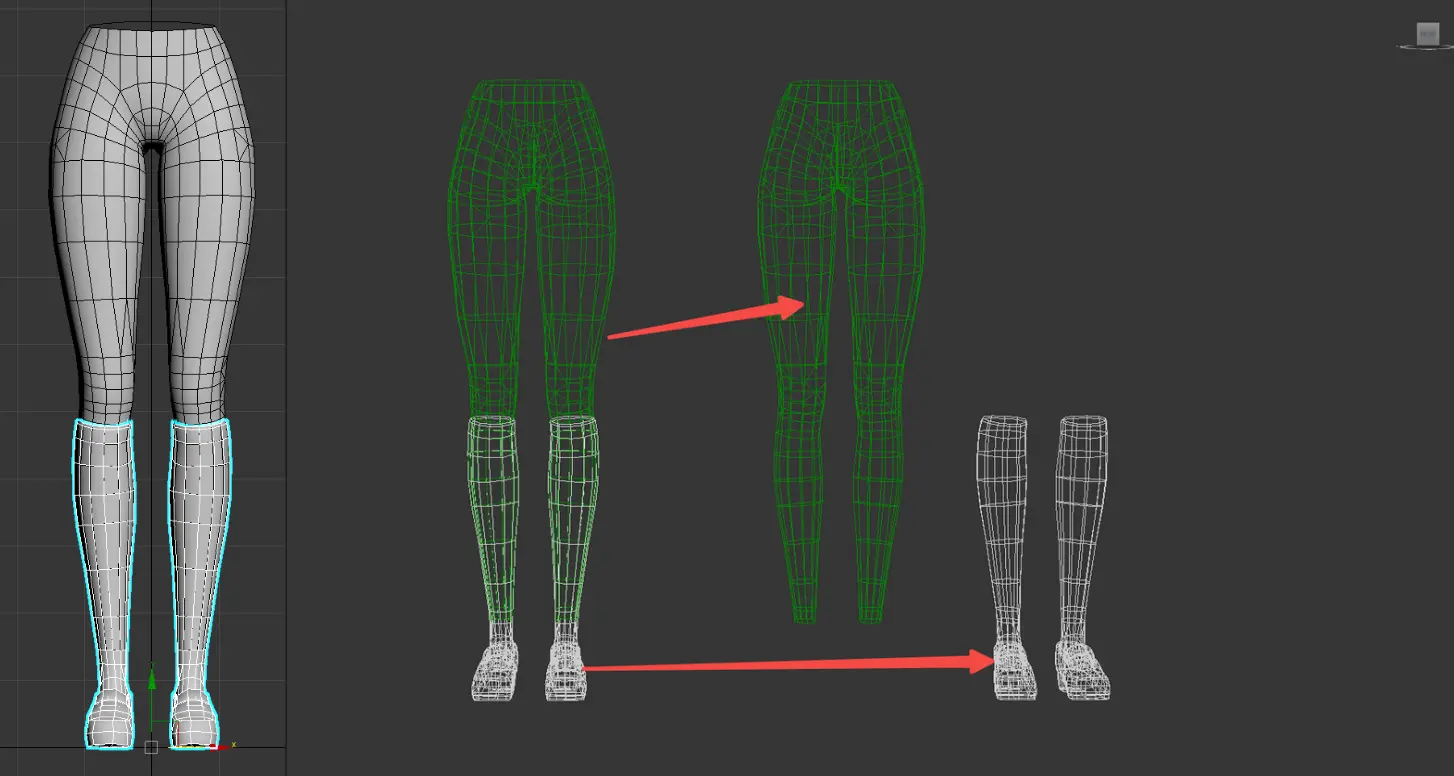
- Socks and Shoes: When the length of socks or shoes does not exceed the knee, they are classified as shoe components.
- The area around the knee and below must align with the base model's topology.
- The model should snugly wrap around the leg base model.
- The foot's base model can be removed if covered by the shoe.
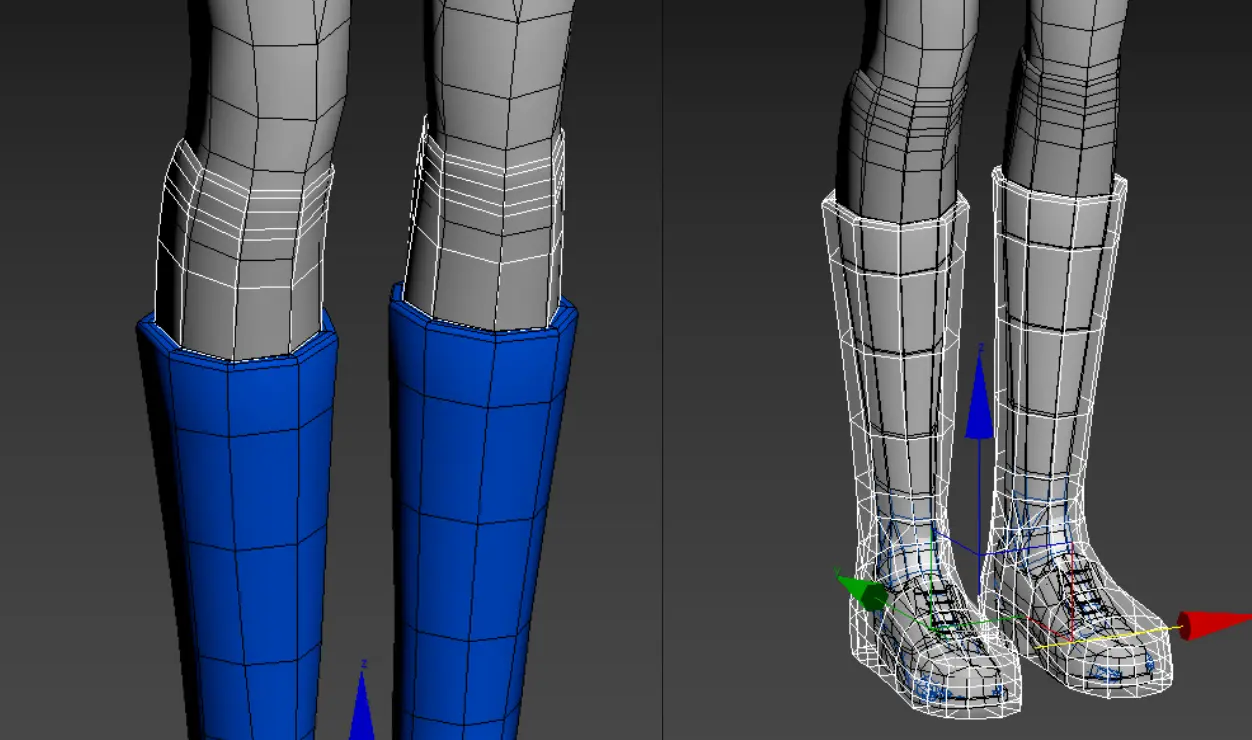
- Shoe Coverage: All shoes need to be covered by pants.
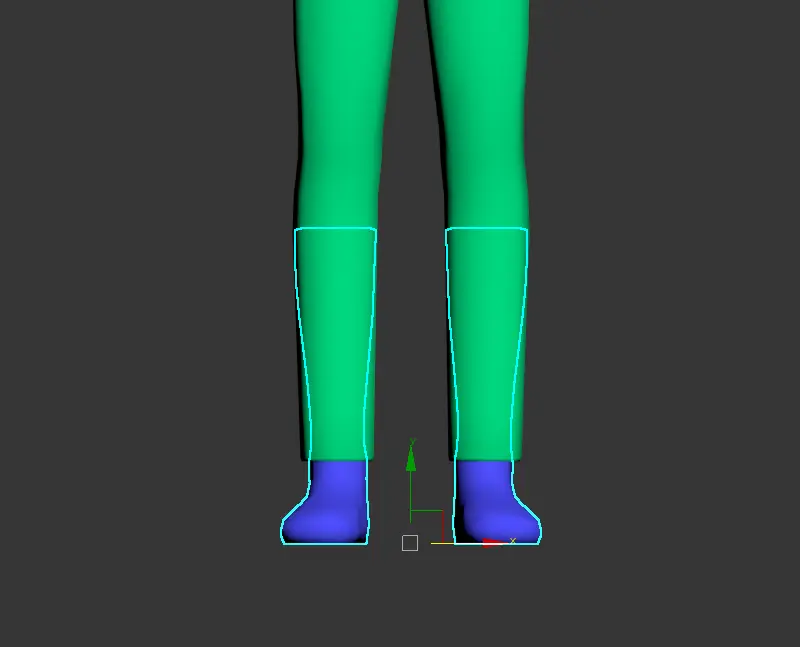

- Shoes themselves must be enclosed within the designated shoe/boot range. Long boots and socks must maintain alignment with the base model's topology.
Gloves Section
- Types of Gloves: Gloves are categorized into long and short types.
- Short gloves end at the hand's cut line.
- Both long and short gloves must not extend beyond the designated glove range.
Hairstyles
Regular Hairstyles
- Typical anime styles.
- Rendering does not support double-sided display; models must be created double-sided.
Strand-Based Hair (Experimental Effect)
- Rendering material does not support double-sided display, thus models need to be made double-sided.
- Covered parts can remain single-sided.
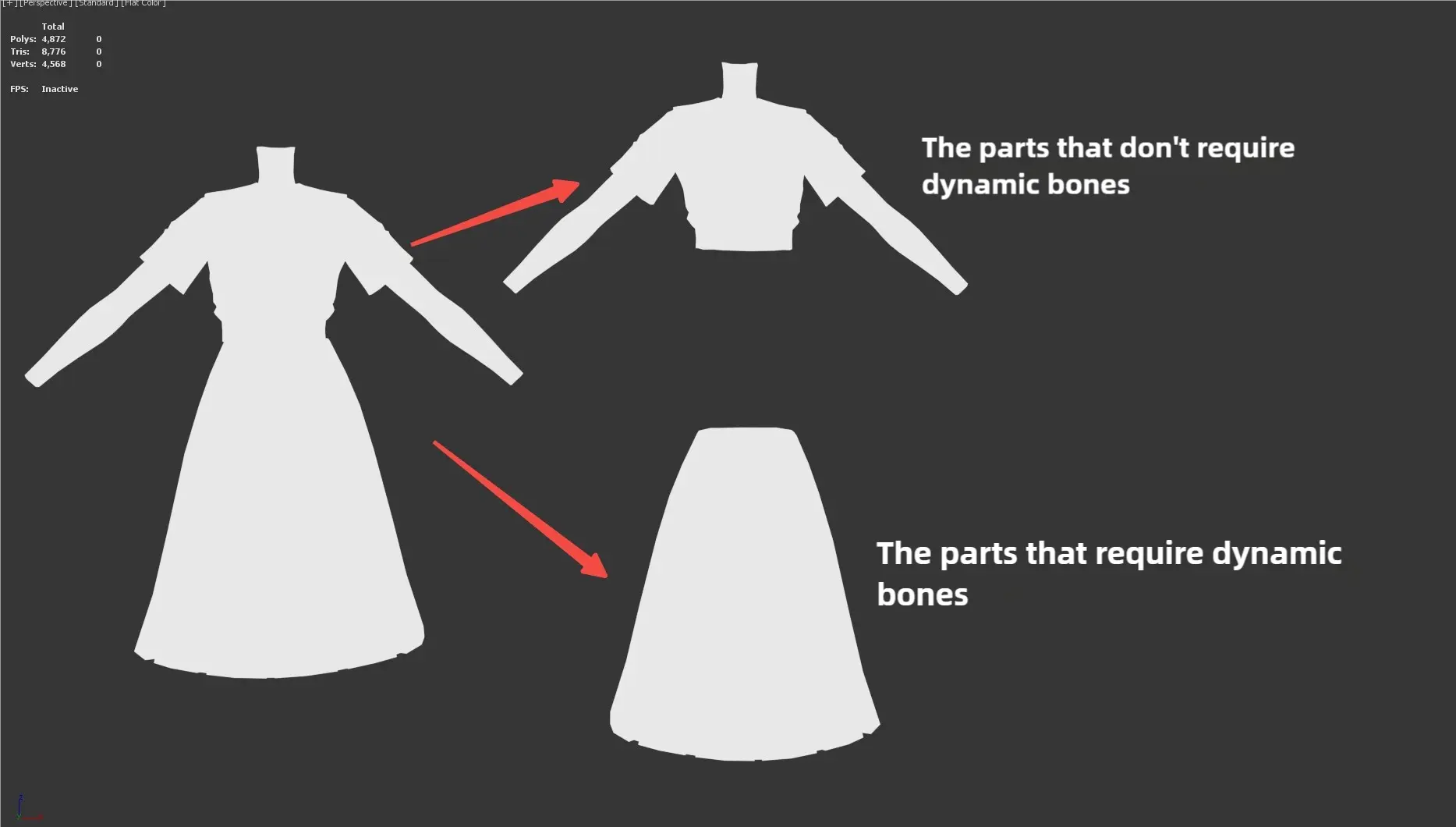
Dynamic Bone Parts (Skirts, Sleeve Edges, Capes)
- Sections requiring dynamic bones must be separately modeled.
- Cuts should be made at the base model's cut lines.
- Only model segmentation is required, facilitating subsequent rigging. Material and UV allocations should follow the model's assigned parts.
- Example: A dress's skirt hem is part of the top component's dynamic bone model.
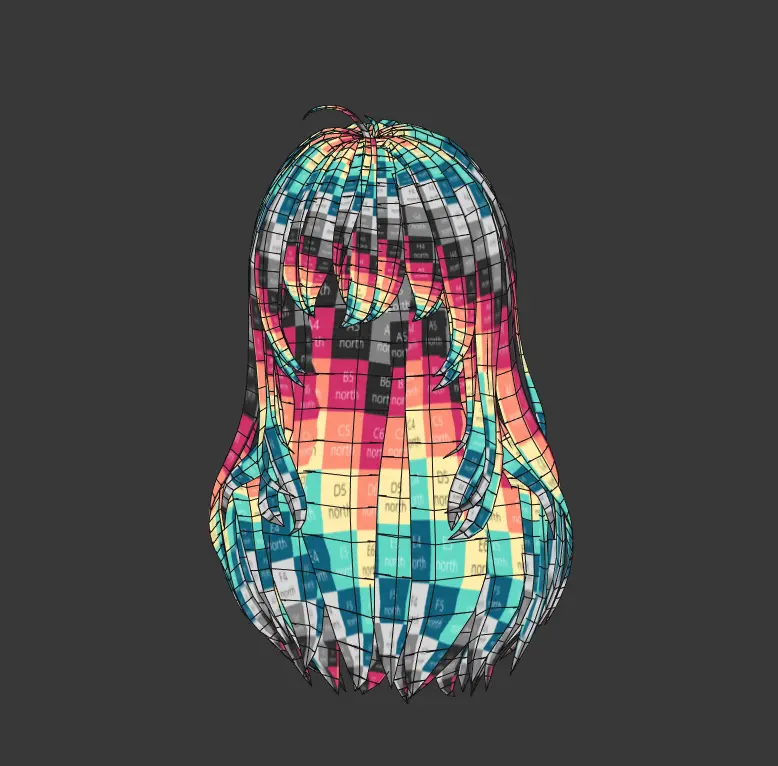
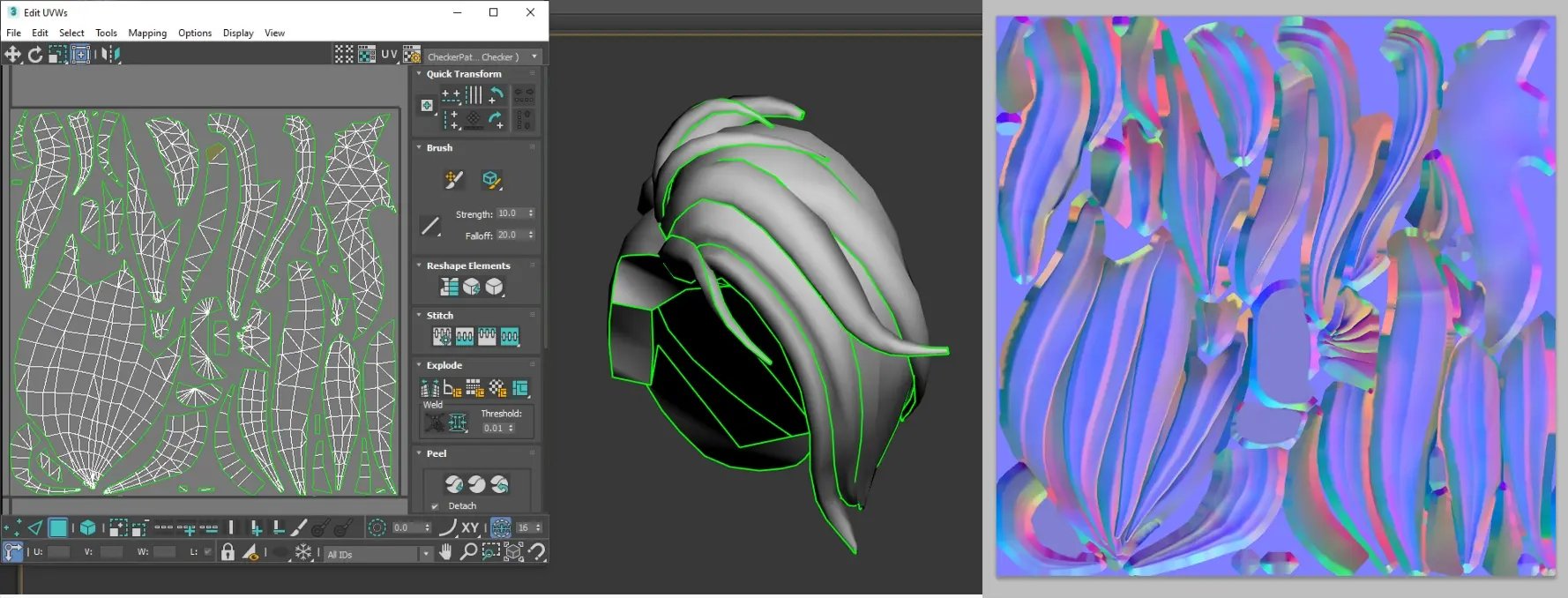
UV Section:
Outfit Resource UV (Clothing + Regular Hairstyles)
UV Segmentation: UVs should be segmented according to different outfit components (top, bottom, shoes, gloves, regular hairstyles).
Base Model UVs: The base model parts should be assigned a separate material ID, and their UVs do not need modification (the model should be merged with the clothing).
Single UV Set Requirement: Only one UV set is needed. Both the base model's skin UVs and the clothing UVs should be placed in UV Channel 1, differentiated by distinct material IDs.
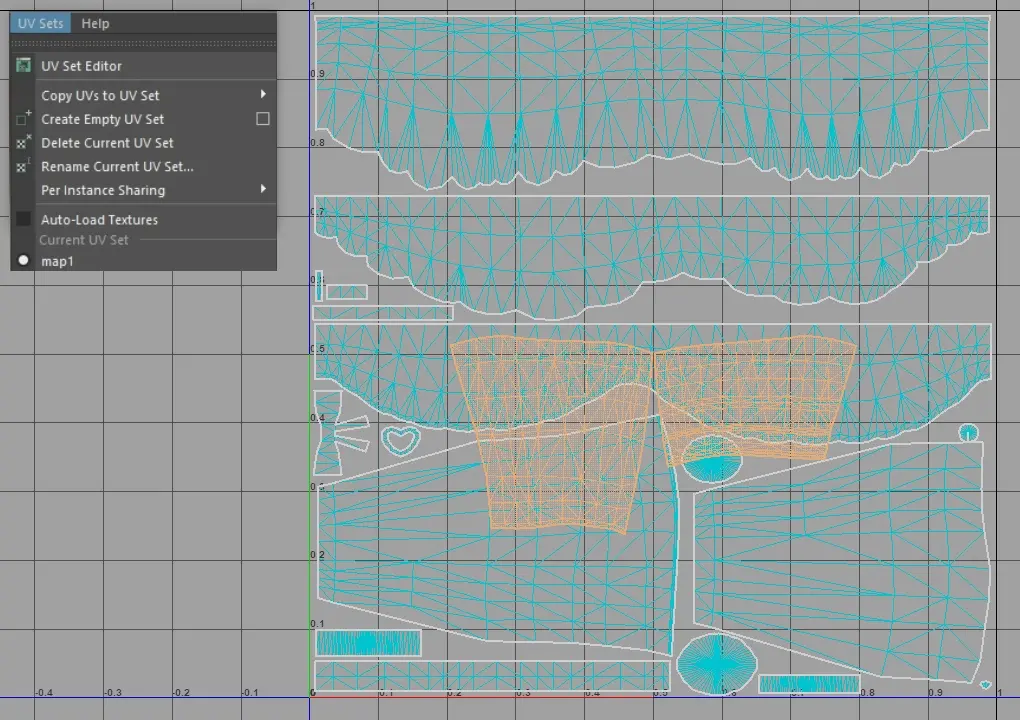
UV Placement: UVs should be positioned within the first quadrant.
Texture Mapping Recommendation: It is recommended to use a single texture set.
UV Integrity: Ensure UVs are complete and have sufficient padding.
Video Tutorial
Strand-Based Hairstyle UV (Experimental Effect)
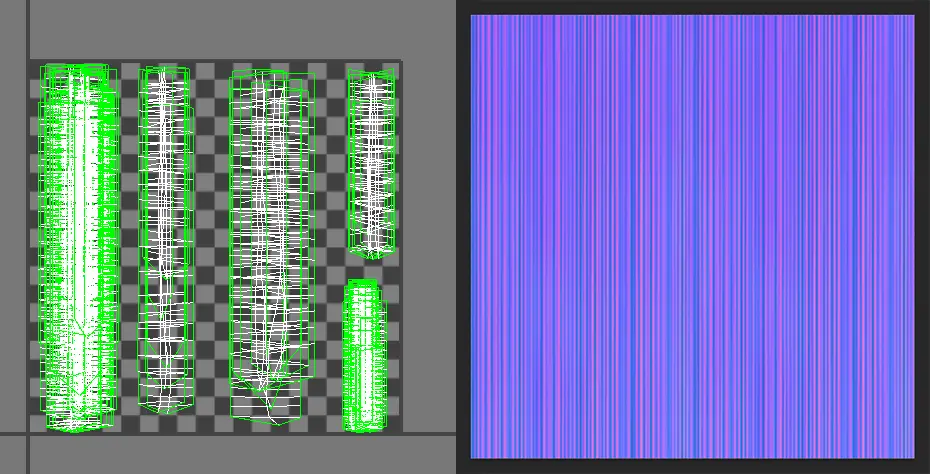
- Multi-UV Requirement: Depending on functional needs, create two UV sets.
UV1:
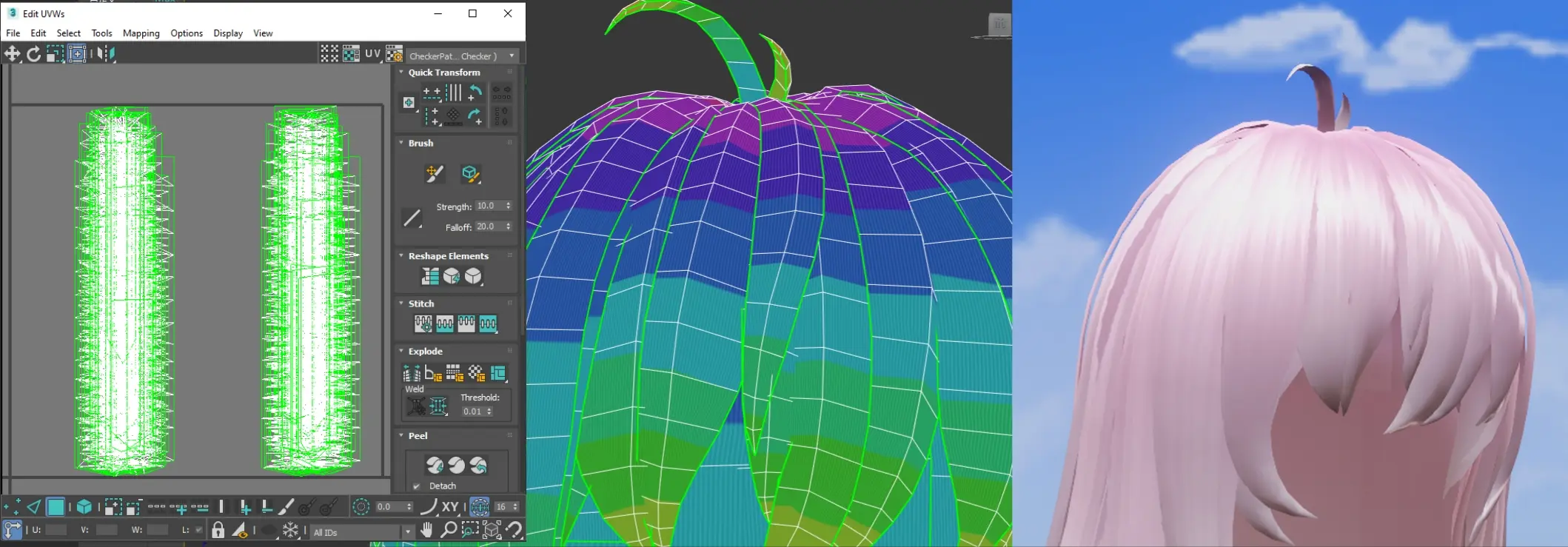
- Gradient and Highlights: To achieve a gradient effect and consistent highlight positioning in Unreal Engine, hair UVs must maintain uniform precision without stretching.
- Align UVs: UVs should be straightened to match provided color maps, ensuring vertical highlights are not stretched and follow the direction of hair flow, giving a natural appearance of hair strands.
- UV Variation: Introduce variability between adjacent hair UVs (the gradient doesn't need to be perfectly aligned), enhancing the richness of the color transition.
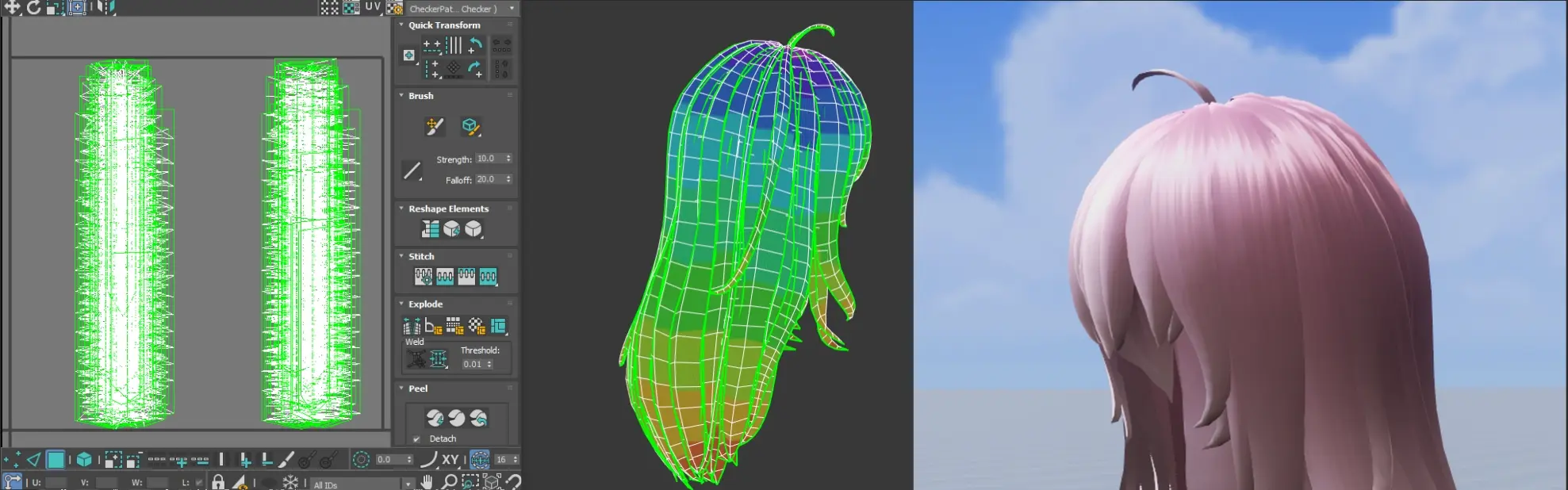
UV2: Hair Normals
- Enhanced Strand Effect: Combine with strand-based normals to enhance the appearance of individual hair strands.
- Full UV Baking: Alternatively, unwrap the entire UV and bake high-resolution normals from the high poly model.
Video Tutorial
Resource Organization
Model Naming
External Models
Naming Format:
SK_Cartoon_Gender_Part_ResourceID_Show- Examples:
- Female Top:
SK_Cartoon_Female_Body_ResourceID_Show - Female Bottom:
SK_Cartoon_Female_Leg_ResourceID_Show - Female Shoes/Socks:
SK_Cartoon_Female_Foot_ResourceID_Show - Female Gloves:
SK_Cartoon_Female_Hand_ResourceID_Show - Female Hair:
SK_Cartoon_Female_HairB_ResourceID_Show
- Female Top:
- Examples:
Dynamic Bone Parts: Append 'Widget(a,b,c)' to connected parts.
Example:
SK_Cartoon_Female_Body_ResourceID_Show_Widget(a,b,c)
Internal Models
Naming Format:
SK_Cartoon_Gender_Part_ResourceID- Examples:
- Female Top:
SK_Cartoon_Female_Body_ResourceID - Female Bottom:
SK_Cartoon_Female_Leg_ResourceID - Female Shoes/Socks:
SK_Cartoon_Female_Foot_ResourceID - Female Gloves:
SK_Cartoon_Female_Hand_ResourceID - Female Hair:
SK_Cartoon_Female_HairB_ResourceID
- Female Top:
- Examples:
Dynamic Bone Parts: Append 'Widget(a,b,c)' to connected parts.
Example:
SK_Cartoon_Female_Body_ResourceID_Widget(a,b,c)
Material Spheres:
- Material Naming: Adhere to material slot standards, assigning materials in DCC software like 3ds Max or Maya, and ensure proper naming.
- Consistent Material Slot Naming: Both external and internal resource materials must follow the same naming rules to avoid material display issues.
| Upper Clothes | ClothUpper |
|---|---|
| Upper Clothes Mask | ClothUpper_Mask |
| Bottom | ClothLower |
| Bottom Mask | ClothLower_Mask |
| Gloves | Glave |
| Gloves Mask | Glave_Mask |
| Shoes | ClothShoes |
| Shoes Mask | ClothShoes_Mask |
| Body Base Model | Body |
| Hair | Hair |
| Hair Accessories | HairAcc |
| Hair Accessories Mask | HairAcc_Mask |
Resource Organization:
Model Checking
- Unit Settings: Verify that units in 3ds Max are set to centimeters.
- Model Coordinates: Ensure the model's coordinates are centered at the world origin and oriented with the -Y axis facing forward.
- Resource Cleanup: Check the resource list for any unused models or empty groups and delete them if present.
- Geometry Issues: Inspect for incorrect double-sided polygons, broken faces, vertices, or polygons with five or more sides.
- Smoothing Groups: Confirm that smoothing groups are correctly set up.
- Model Normals: Check that the normals at each junction are consistent with those of the base model.
- Material Assignment: Ensure that each part has been assigned a material and that the material names are correct.
- UV Set Count: Verify that the number of UV sets is correct.
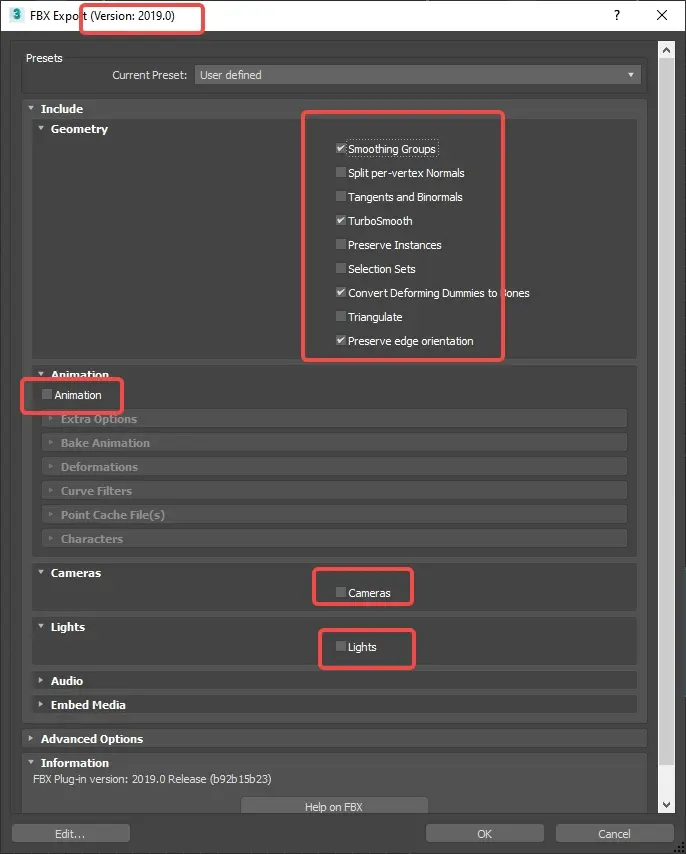
FBX Output
- FBX Export Settings:
- The export of the model at this stage should only be used for material effect verification or for the creation of related textures.
 Editor Doc
Editor Doc